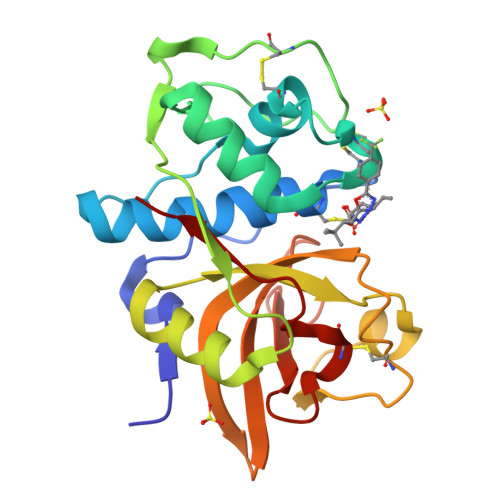
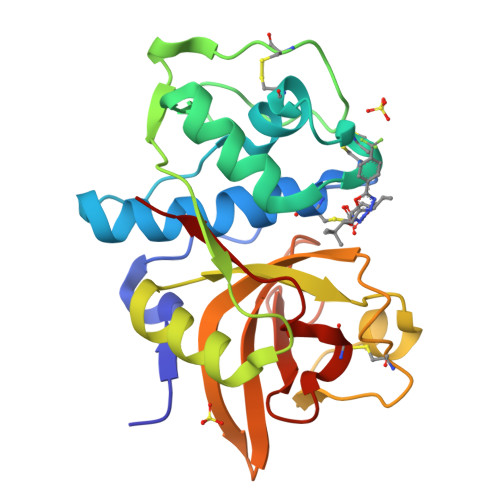
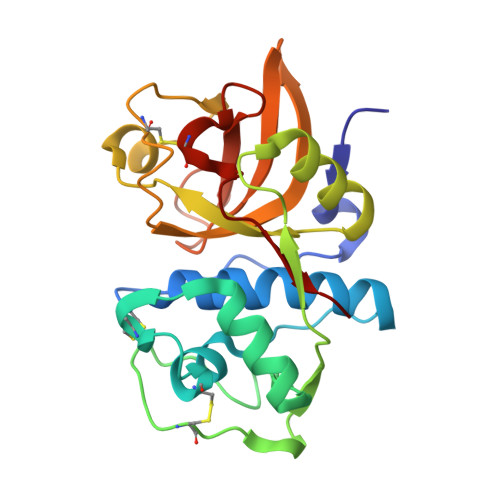
P(2)-P(3) conformationally constrained ketoamide-based inhibitors of cathepsin K.
Barrett, D.G., Boncek, V.M., Catalano, J.G., Deaton, D.N., Hassell, A.M., Jurgensen, C.H., Long, S.T., McFadyen, R.B., Miller, A.B., Miller, L.R., Payne, J.A., Ray, J.A., Samano, V., Shewchuk, L.M., Tavares, F.X., Wells-Knecht, K.J., Willard, D.H., Wright, L.L., Zhou, H.Q.(2005) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 3540-3546
- PubMed: 15982880
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.05.062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YT7 - PubMed Abstract:
An orally bioavailable series of ketoamide-based cathepsin K inhibitors with good pharmacokinetic properties has been identified. Starting from a potent inhibitor endowed with poor drug properties, conformational constraint of the P(2)-P(3) linker and modifications to P(1') elements led to an enhancement in potency, solubility, clearance, and bioavailability. These optimized inhibitors attenuated bone resorption in a rat TPTX hypocalcemic bone resorption model.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, USA.